Relation to other fields:-
Prerequisites:-
Mathematics provides a compact and exact language used to describe of the order in nature. This was noted and advocated by Pythagoras,Plato,Galileo, and Newton.
Physics uses mathematics[44] to organize and formulate experimental results. From those results, precise orestimated solutions, quantitative results from which new predictions can be made and experimentally confirmed or negated. The results from physics experiments are numerical measurements. Technologies based on mathematics, like computation have made computational physics an active area of research.
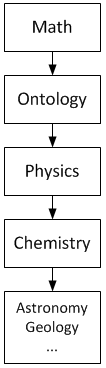
Ontology is a prerequisite for physics, but not for mathematics. It means physics is ultimately concerned with descriptions of the real world, while mathematics is concerned with abstract patterns, even beyond the real world. Thus physics statements are synthetic, while mathematical statements are analytic. Mathematics contains hypotheses, while physics contains theories. Mathematics statements have to be only logically true, while predictions of physics statements must match observed and experimental data.
The distinction is clear-cut, but not always obvious. For example, mathematical physics is the application of mathematics in physics. Its methods are mathematical, but its subject is physical. The problems in this field start with a "mathematical model of a physical situation" (system) and a "mathematical description of a physical law" that will be applied to that system. Every mathematical statement used for solution has a hard-to-find physical meaning. The final mathematical solution has an easier-to-find meaning, because it is what the solver is looking for.
Physics is a branch of fundamental science, not practical science. Physics is also called "the fundamental science" because the subject of study of all branches of natural science like chemistry, astronomy, geology and biology are constrained by laws of physics,similar to how chemistry is often called the central science because of its role in linking the physical sciences. For example, chemistry studies properties, structures, and reactions of matter (chemistry's focus on the atomic scale distinguishes it from physics). Structures are formed because particles exert electrical forces on each other, properties include physical characteristics of given substances, and reactions are bound by laws of physics, like conservation of energy, mass and charge.
Physics is applied in industries like engineering and medicine.




No comments:
Post a Comment